

PETRA YVONNE ENGLISH
Health Care & Human Body
Good health means a longer and happier life. Health, together with love, is the most precious gift that people have.
How to prevent illnesses/diseases.
To stay fit and keep our mind and body in good balance, we should:
- Eat Healthy Foods: Choose foods that are good for your health and provide essential nutrients.
- Stay Active: Take part in different sports or activities. Avoid spending too much time sitting in front of screens like the TV, computer, phone, or playing video games.
- Handle Stress: Try to avoid situations that make you feel worried or stressed. Stay away from alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs.
- Get Outside: Spend time in the fresh air and move around regularly.
- Sleep Well: Make sure you have a regular sleep routine and get enough rest.
- Stay Positive: Try to see things in a hopeful and optimistic way. Cultivate a positive outlook on life.
Everyone in our country has the right to choose a doctor. Medical care is provided for our
citizens from birth to death.
Children’s Diseases
After birth, each child is vaccinated against:
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Polio
- Chickenpox (smallpox)
- Mumps
Each schoolchild is under medical supervision, which means they have to undergo a series
of preventive medical and dental check-ups, during which:
- Their body is examined.
- Their teeth are checked.
- Their eyesight is tested.
QUESTION TIME
PART 1
- Why should people take care of their health?
- What rules should we follow to stay in good shape?
- Which diseases can affect small children?
Most often, we suffer from common infections like:
- A cold and a sore throat – our nose is running or it is blocked. We sneeze and cough a lot.
- Tonsillitis – our glands are swollen and we cannot swallow.
- Flu – we have achy joints, high temperature, headache, and physical fatigue.
- A chest infection – we have difficulty breathing.
Common infections are very contagious. We try to recover from them on our own. We:
- Stay in bed,
- take pills, drops, and vitamins,
- keep warm,
- sweat a lot,
- drink herbal tea with honey or lemon,
- the best thing we can do is to simply rest in bed completely.
After a couple of days, we should feel better again. But if we still feel unwell, we finally decide
to see our local doctor, who is called a General Practitioner (GP).
QUESTION TIME
PART 2
- Can you list any common infections and their symptoms?
- Give some tips on how to recover from common infections without seeing a doctor.
- What is another term for a local doctor?
At the doctor’s office (At the doctor’s)
Firs, we have to wait in the waiting room until the nurse calls us into the examination room.
The nurse has to locate our medical record and asks to see our insurance card. Their other duties include:
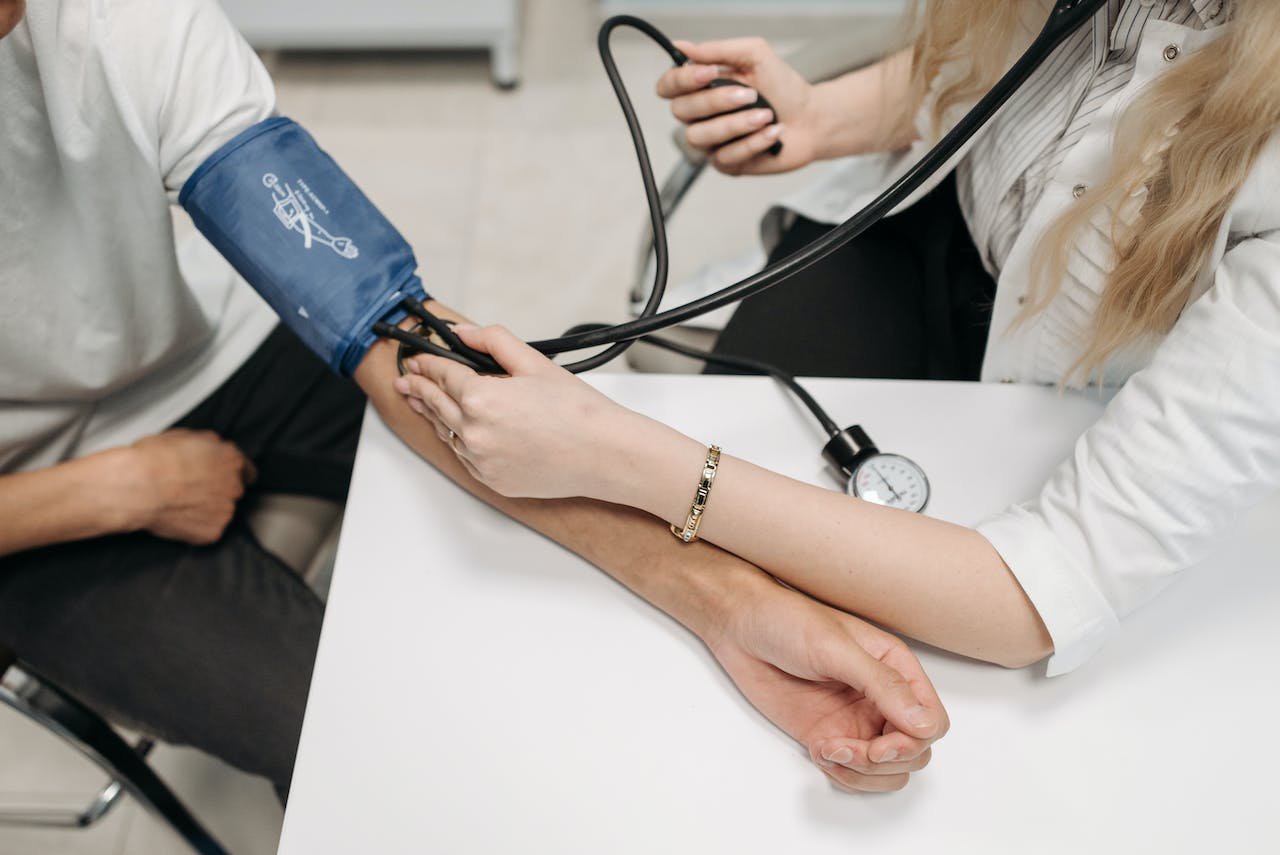
- taking the temperature
- checking the blood pressure
- taking/drawing blood
- testing the urine
Then we are ready to enter the examination room/doctor’s office/surgery. The doctor
usually asks us how we feel, what problems we are having, or what’s bothering us. If we have a headache, a sore throat, a cold, or a cough, we need to mention it. Then the doctor examines us. He:
- Listens to our lungs and heart.
- Asks us to take a deep breath or hold our breath according to his instructions.
- Makes a diagnosis.
- Writes a prescription for us.
- Schedules the next check-up.
Then we go to the drugstore (AmE) / chemist’s (BrE) where we can get:
- Antibiotics, gargle, cough syrup, vitamins, ointments, nose drops, and painkillers.
- We need to take medicine according to the doctor’s advice, and for a short time, we may be unable to attend school or work.
- Every household should have a first-aid kit. It should contain: a clinical thermometer, sterile gaze pads, bandages, Band-Aids, scissors, and some pain relievers.
QUESTION TIME
PART 3
- When do you go to see the doctor?
- What questions do doctors ask their patients?
- Describe what happens in a doctor’s surgery / office.
- What is the nurse´s job?
- What medicine can we take at the pharmacy / at the chemist’s / drugstore?
- What items does a first-aid kit contain?
Critical illnesses
Sometimes the situation may be critical and requires special treatment in a hospital.
Here are some serious illnesses that require special treatment:
- heart attack, pneumonia, jaundice, stroke, concussion, blood poisoning, insomnia, salmonellosis, appendicitis, breaking an arm or a leg
In the hospital, injured people are examined and X-rayed. Very serious cases are immediately operated on in the operating room (AmE) / the operating theatre (BrE).
Doctors who work in hospitals are usually referred to as specialists, for example:
- surgeons, psychiatrists, internists, ophthalmologists, gynecologists, dermatologists, pediatricians
Illnesses of Civilization
Many people suffer from:
- pollen allergies, food allergies, diabetes, obesity, cancer.
- Cancer is one of the biggest threats nowadays. Every year, more and more people of all ages are diagnosed with tumors of all types.
- Daffodil Day is a public collection organized to raise money to provide support for people with cancer and their families.
QUESTION TIME
PART 4
- Which diseases do you think are the most serious? Why?
- Can you name any medical specialists in English?
- Have you ever had to go to the hospital? If so, what for?
- How long did you stay there?
- Which illnesses related to modern lifestyles can people suffer from?
(Illnesses of Civilization) - What is Daffodil Day?
Civilization Diseases and Epidemics
The latest global threat is the COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic. It was first identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. While most people who
recover from COVID-19 experience mild symptoms, it can also lead to severe illness and
even death. The virus primarily spreads when an infected person is in close contact with
another person.
Symptoms of COVID-19 are variable: fever, cough, fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of
smell and taste.
Preventive measures include: physical or social distancing, ventilation of indoor spaces, covering your mouth and nose when you caught or sneeze, handwashing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face, the use of face masks in public.
Internal Organs of the Human Body
Heart, lungs, liver, stomach, kidneys, brain, small intestine, large intestine (colon), gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, bladder, etc.
Parts of the Human Body
head, hair, forehead, eyebrows, eyes, nose, cheeks, ears, mouth, lips, teeth, tongue, chin,
neck, shoulders, arms, elbows, wrists, hands, fingers, chest, breast, abdomen, navel (belly
button), hips, thighs, knees, legs, ankles, feet, toes
Fingers: thumb, index finger, middle finger, ring finger, pinky finger
At the Doctor – Useful Phrases
- Questions Asked by Doctors and Nurses
What problems are you having? / What’s wrong with you?/ What’s bothering you? - Did you vomit?
- Breathe deeply / Breathe quietly / Stop breathing. / Breathe in. / Breathe out.
- Do you have an insurance card?
- Do you have high blood pressure?
- Do you have any pre-existing conditions?
- Where does it hurt?
- Is it painful?
- Do you have breathing difficulties?
- The next check-up will be in 5 days.
- It is not serious.
- Did you have a fever?
- Are you allergic to anything?
- I will write you a prescription.
- You will be taking the pills three times a day.
- Are you currently taking any medication?
- You need complete bed rest for a week.
- You will be admitted to the hospital.
- I will write you a prescription.
QUESTION TIME
PART 5
- Name some symptoms of COVID-19.
- What preventive measures should we follow to protect ourselves from the
coronavirus? - Name some internal organs of the body.
- Can you mention any parts of the human body? Let’s start from the head.
- What phrases or questions might we hear at the doctor’s?
vocabulary
1. illness / disease / sickness skchoroba
2. healthy nutrition skzdravá výživa
3. avoid stress skvyhýbať sa stretu
4. suffer from sktrpieť niečím
5. get over / overcome / go through skprekonať
6. waiting room skčakáreň
7. breathe deeply skzhlboka sa nadýchnuť
8. to transmit / pass sth. on skprenášať / vírus
9. general practitioner / GP skobvodný lekár
10. paediatrician skdetský lekár
11. surgeon skchirurg
12. dermatologist skkožný lekár
13. internist skinternista
14. psychologist skpsychológ
15. dentist skzubár
16. cardiologist skkardiológ
17. drug addicted skdrogovo závislý
18. to undergo treatment skpodstúpiť liečbu
19. medical record skzdravotná karta
20. to take blood skzobrať krv
21. pollen allergy skpeľová alergia
22. infected person sknakazená osoba
23. flu / influenza skchrípka
24. check up skpreventívna prehliadka
25. eyesight skzrak
26. to recover skzotaviť sa, uzdraviť sa
27. first-aid kit sklekárnička
28. ointment skmastička
29. thermometer skteplomer
30. adhesive plaster sknáplasť
31. drops skkvapky
32. bandage skobväz
33. painkiller skliek od bolesti
34. cough syrup sksirup od kašľa
35. insurance card skkartička poistenca
36. consulting room skmiestnosť u sestričky
37. to ache / to hurt skbolieť
38. damage skpoškodenie, škoda
39. to check the blood pressure skskontrolovať krvný tlak
40. curable skliečiteľný
41. incurable skneliečiteľný
42. to be in a good shape skbyť v dobrej forme
43. to be allergic to sth. skbyť alergický na niečo
44. a lack of physical activities sknedostatok pohybu
45. insufficient sleep sknedostatok pohybu
46. sedentary work sksedavé zamestnanie
47. overeating skprejedanie sa
48. to be caused by skbyť spôsobené
49. catching sknákazlivé, chytľavé
50. treatment / cure skliečba
51. doctor´s surgery / doctor´s office skordinácia
52. arm skruka (celá)
53. armpit skpodpazušie
54. elbow sklakeť
55. wrist skzápästie
56. palm skdlaň
57. little finger / pinkie skmalíček
58. ring finger skprsteník
59. middle finger skprostredník
60. index finger skukazovák
61. thumb skpalec

62. skin skkoža
63. eye skoko
64. eyebrow skobočie
65. eyelashes skmihalnice
66. eyelid skviečko
67. forehead skčelo
68. jaw sksánka, spodná čeľusť
69. tongue skjazyk
70. teeth skzuby
71. lips skpery
72. chin skbrada
73. cheeks sklíca
74. waist skpás
75. leg sknoha (celá)
76. foot skchodidlo
77. calf sklýtko
78. thigh skstehno
79. ankle skčlenok
80. knee skkoleno
81. toe skprst na nohe
82. neck skkrk
83. throat skhrdlo
84. internal organs skvnútorné orgány
85. lungs skpľúca
86. kidneys skobličky
87. liver skpečeň
88. brain skmozog
89. heart sksrdce
90. muscles sksvaly
91. back skchrbát
92. breast / chest skhruď
93. hips skboky
94. injuries skzranenia
95. bruiseskmodrina, pomliaždenina
96. blisterskpľuzgier
97. swollen skopuchnutý
98. twisted/ sprained skvyvrtnutý
99. bleeding skkrvácajúci
100. broken skzlomený
101. burn skpopálenina
102. common illnesses skbežné choroby
103. chest infection skzápal priedušiek
104. earache skbolesť uší
105. stomachache skbolesť brucha
106. backache skbolesť chrbta
107. toothache skbolesť zubov
108. serious diseases kvážne choroby
109. cancer skrakovina
110. Parkinson´s disease skParkinsonova choroba
111. Parkinson´s disease skAlzheimerova choroba
112. heart attack skinfarkt
113. stroke skmozgová príhoda
114. pneumonia skzápal pľúc
115. insomnia sknespavosť
116. blood poisoning skotrava krvi
117. jaundice skžltačka
118. hypertension skvysoký krvný tlak
119. children´s diseases skdetské choroby
120. measles skosýpky
121. polio skdetská obrna
122. smallpox / chickenpox skkiahne
123. whooping cough skčierny kašeľ
124. symptoms skpríznaky
125. high temperature skvysoká teplota

126. sweating skpotenie sa
127. cough/ coughing skkašeľ
128. to sneeze skkýchať
129. sore throat skboľavé / zapálené hrdlo
130. aching joints skboľavé kĺby
131. total bed rest skúplný kľud
132. diarrhoea skhnačka
133. vomiting skvracanie
134. running nose sknádcha
135. blocked nose skupchatý nos
136. blow one´s nose skvysmrkať sa
137. loss of smell skstrata čuchu
138. loss of taste skstrata chuti
139. constipation skzápacha
140. nausea skžalúdočná nevoľnosť
141. spots skvyrážky, fľaky, škvrny
142. high / low blood pressure skvysoký / nízky tlak
143. face mask skrúško
144. keep social distance skdodržiavať odstup
145. fatigue / tiredness skúnava, vyčerpanosť
146. breathing difficulties skdýchacie ťažkosti
147. take temperature skodmerať teplotu
148. take antibiotics skužívať antibiotiká
149. to examine a patient skvyšetriť pacienta
150. to listen to one´s heartbeat skpočúvať srdce
151. to listen to one´s breathing skpočúvať dýchanie
152. to operate skoperovať
153. to prescribe some medicine skpredpísať lieky
154. ward skoddelenie v nemocnici
155. instead of sknamiesto niečoho
156. side effects skvedľajšie účinky
157. to overdose skpredávkovať sa
158. prescription sklekársky recept
159. hectic life skhektický život
160. under the supervision of skpod kontrolou, dohľadom
161. preventive check-ups skpreventívne prehliadky

Share this with your friends👉
© 2025 Petra Yvonne English – English online







